
Experimental Process & Results
Our Idea
While artificial nests have become an important conservation tool, current designs often fall short in terms of durability, safety, or environmental friendliness. Instead of using glass fiber as a reinforcement, this experiment investigated the use of more environmentally friendly materials: natural fibers.
Expectations of the Experiment
1. Hornbills can have nests without relying on tree holes, helping to protect both the great hornbill and large trees.
2. The use of more natural and environmentally friendly materials for nest construction.
PURPOSES
To determine natural materials that can replace fossil-based materials in the creation of artificial bird nests for hornbills, specifically composite materials.
Composite materials consist of a continuous matrix and reinforcement. Materials that can be transformed into natural composites have two parts:
-
Reinforcement: Natural fibers
-
Continuous matrix: Unsaturated polyester resin, including those derived from recycled PET plastic bottles
METHODS
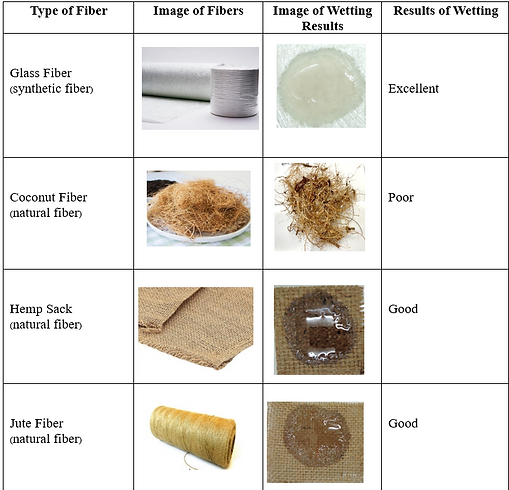
Wetting Test
Purpose: to determine the absorbability of the natural fibers.
Results: Of these fibers, pineapple fiber, banana fiber, sisal fiber, and water hyacinth showed good wetting properties. However, these fibers needed to be woven, which complicates their use in sheet formation. In contrast, hemp fiber is the most effective option as the form was already woven, providing good properties when combined with polyester resin for making artificial nests. However, all of the fibers that demonstrated good wetting results will still be tested for the subsequent tests.




Mechanical Tests
3-Point Bending Test
Purpose: To evaluate the material’s ability to resist bending and deformation.
Results: The bending test revealed that different types of natural fibers displayed varying max load and flexural strength. Among the tested fibers, the composite materials made from hemp fiber and pineapple fiber demonstrated greater flexural strength compared to the other fibers tested. However, hemp fiber was chosen because it was less costly when compared to pineapple fiber. As a result, for the next tests, only hemp fiber was tested.


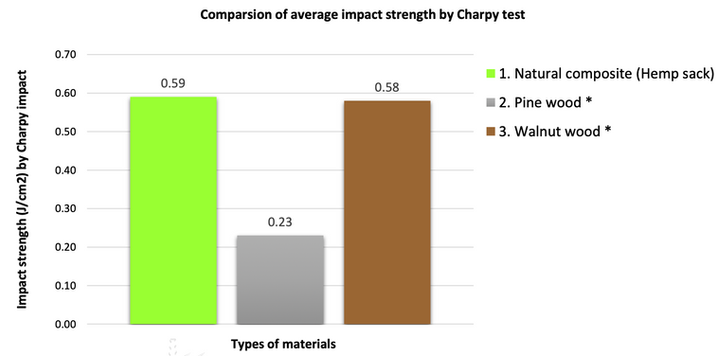
Charpy Impact Test
Purpose: To determine the composite material’s ability to withstand impact.
Results: Hemp fibers showed comparable results to walnut wood and
better results than pine wood.

OVERALL RESULTS

Overall, hemp fibers had better results than other natural fibers. Though the impact strength is not comparable to that of glass fiber, it is comparable to wood. The impact resistance improved by increasing the number of layers of hemp fiber. However, increasing the number of layers increases the weight. As a result, six layers of hemp fiber were selected for our prototype to create artificial nests. These tests together proved that the artificial nest made from hemp fiber composite is safe and an alternative to glass fiber.
Weathering Test
Purpose: To determine the durability of the nest. Specifically, the QUV weathering test determines the composite's resistance to degradation from sunlight, rain, and humidity in outdoor environments. The test ensures artificial nests stay strong and safe for long periods. The test compared hemp fiber composites to conventional glass fiber composites.
Results: The hemp fiber can last 4000 hours without deformation and will last over 10 years.


Ventilation Test
Purpose: The materials used to build artificial bird nests were studied to determine how they affect the nest microclimate, specifically temperature and humidity inside hornbill nests. We compared a hemp fiber composite nest to a wooden artificial nest.
Results: The difference in nest temperature between wooden and composite nests (during summer) is around 1-2 °C.

Results 2025

Artificial Nests Being Built

